shoulder tests labral tears|positive shoulder labral tear test : maker Introduction. Shoulder Exam. In examining a patient with a painful shoulder we should start with a general inspection, looking for musculoskeletal abnormalities and any associated functional deficits. Then, we can carry on some . Resultado da 6 de dez. de 1997 · View credits, reviews, tracks and shop for the 1997 DVD release of "Out Loud" on Discogs.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Welcome to Old School RuneScape! Relive the challenging l.
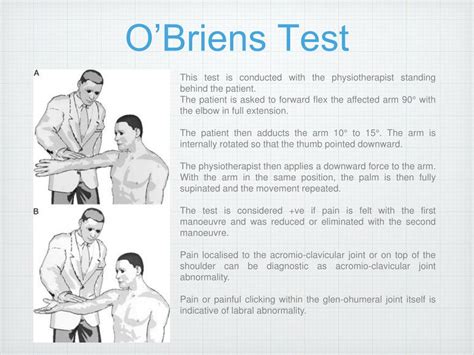
The O’Brien test is a simple procedure that healthcare professionals use to assess shoulder pain. It can detect a cartilage (labral) tear or an acromioclavicular (AC) joint problem. .Diagnosing Labral Tears of the Shoulder. To evaluate for a possible shoulder labrum tear, a Penn orthopaedic specialist will examine your shoulder, conduct several physical tests to check your range of motion, take a full health history .
The purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate potential labral (SLAP Lesion) or acromioclavicular lesions as cause for shoulder pain. [1] [2] .Introduction. Shoulder Exam. In examining a patient with a painful shoulder we should start with a general inspection, looking for musculoskeletal abnormalities and any associated functional deficits. Then, we can carry on some .
The best tests available to make the diagnosis of a labral tear are magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans or a test called a CT-arthrogram (the latter is a CAT scan preceded by an arthrogram where dye is injected into the shoulder). . The most common symptoms of a shoulder labrum tear are shoulder pain, instability and, in some cases, a feeling of grinding, locking or catching while moving the shoulder. These symptoms may vary depending .
This test also called labral crank test or compression rotation test is used to identify glenoid labral tears and assess an unstable superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) lesions. [1]O’Brien’s Test is a special orthopaedic/orthopedic test for the shoulder that attempts to test specifically for glenohumeral joint labral tears (and more specifically for SLAP Lesions; .
For example, orthopaedic surgeons can now use miniaturized instruments and cameras (arthroscopic surgery) to see inside a joint. This enables them to identify and treat a shoulder injury called a glenoid labrum tear, also known as a .
Often associated with anterior labral tears and shoulder instability. . Specific tests include: Speed’s test; Yergason’s test; Biceps load test II; If one of the three tests is positive, this will result in a sensitivity of about 75%. But if all .Positive Test [edit | edit source]. Clunk or Grinding: A clunking or grinding sensation is felt or heard, indicating a possible labral tear. Pain: The presence of pain during the maneuver can also indicate a positive test. Significance [edit | edit source]. Labral Tear: The test is particularly useful for identifying superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) lesions.This test also called labral crank test or compression rotation test is used to identify glenoid labral tears and assess an unstable superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) lesions. . Munro W, Healy R. The validity and accuracy of clinical tests used to detect labral pathology of the shoulder-a systematic review. Manual Therapy 2009; 14(2 . Here I demonstrate for you in this video how to perform the O'Brien's Test and talk about what a positive test is and what it means. 👉MedBridge: Online CEUs.
This enables them to identify and treat a shoulder injury called a glenoid labrum tear, also known as a labral tear. Anatomy. The shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint made up of three bones: The humerus (upper arm bone) The scapula (shoulder blade) The clavicle (collarbone) . Do several physical tests to check range of motion, stability, and pain.

High Frequency wood moisture meter suppliers
speed's test vs o'brien's
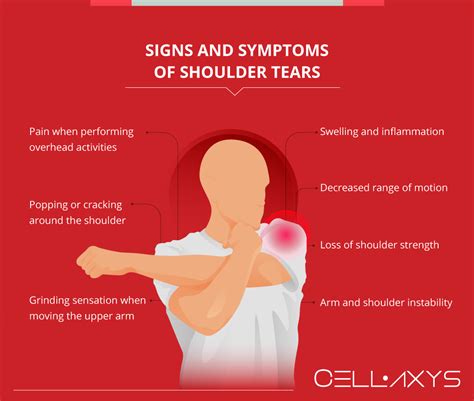
A tear may also occur from a blow to the shoulder or from a fall. General wear from years of use can also make the shoulder labrum more susceptible to tears. Shoulder labral tears may cause pain in the joint while you are performing overhead activities such as placing items on a shelf or playing sports such as basketball or tennis. You may also . A SLAP lesion (Superior Labrum from Anterior to Posterior tear) generally occurs as result of overuse injury to the shoulder in overhead athletes or traumatic falls in older patients and can result in deep shoulder pain and biceps tendonitis.
Type 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. Type 1 tears are often seen in people who are middle-aged or older. Type 2: This is the most common SLAP tear type. In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. Type 3: Torn labrum tissue is caught in the .They included tests not only for shoulder labral tears but for shoulder impingement, scapular positioning, range of movement, and shoulder instability, among other pathologies. The 2010 review found that the reliability of physical tests for diagnosing shoulder pain . Take the labrum tear test. There are 4 tests your doctor will conduct on your shoulder that specifically identify a labrum tear. If you respond in pain to any of the test, your test will be considered a pass for that specific test. . "Labrum Tear of The Shoulder." Howard J Luks MD. N.p., n.d. . 13 Oct. 2016. More References (1) Dr. Tarek S .
Hawkins' test: Forward flexion of the shoulder to 90 degrees and internal rotation: Supraspinatus tendon impingement: . Glenoid labral tears are assessed with the patient supine. The patient's .
Shoulder special tests can be useful for evaluating and diagnosing shoulder pathology such as impingement, biceps tenonopathy, instability, rotator cuff tears, and injury to the labrum. These are some of the most common shoulder special tests performed in . The glenoid labrum is integral to shoulder stability and can be difficult to assess clinically. Whilst it is a single anatomical structure, damage to different regions results in very different clinical manifestations. . The active compression test: a new and effective test for diagnosing labral tears and acromioclavicular joint abnormality .When the tear is at the back of the shoulder ( posterior ) (6 o'clock to 11 o'clock), it is a Reverse Bankart tear : . When a tear is a combination of Bankart , Reverse Bankart tear and SLAP tear , it is known as a 270 degree tear: . Chronic, longstanding labral tears can give rise to paralabral cysts.This is where the tear becomes a one-way valve so joint synovial fluid seeps out of the .
A SLAP tear of the shoulder is an injury to the labrum of the shoulder joint. SLAP tears typically cause pain when performing overhead activities. . There are several tests a skilled examiner can perform to detect .A shoulder labrum tear is where there is damage to the ring of cartilage at the shoulder joint. Glenoid labrum tears often cause shoulder pain and instability. Shoulder Pain. . These tests are not always accurate and in some cases .
Labral tears to the shoulder A labral tear in the shoulder refers to an injury or damage to the labrum, which is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the shallow socket of the shoulder joint. Common causes of labral tears in the shoulder include: Trauma. Repetitive movement. Age. Labral tears to the hip
Shoulder labral tears are a common acute injury. Learn about the Labrum, why tears occur, the best treatment options, and ways to prevent future injuries. . In order to do an evaluation, the Physician will perform several common orthopedic special tests that indicate a labral tear could be present. These common tests include Obrien’s test . Posterior Labral Tear Neurovascular Disorders . flex elbow to 90°, hold shoulder at 20° elevation and 20° extension. Internally rotate shoulder to near maximum holding the wrist by passively lifting the dorsum of the hand away from the lumbar spine – then supporting the elbow, tell patient to maintain position and release the wrist while .
special tests for shoulder labrum
Explanation of O'Brien's Test in orthopedic shoulder examination including involved tissues, test postion, test movement, etc. plus video demonstration. Skip to content. . superior labral tear from anterior to posterior). A false positive may occur if there is an injury to the rotator cuff or acromioclavicular (AC) joint. Involved Structures . This type of shoulder labral tear occurs at the top (“superior”) of the glenoid labrum where it connects to the biceps tendon, and it extends in a curve from the chest (“anterior”) to the back (“posterior”). SLAP lesions are considered as separate entities from other labral tears because the superior labrum is the attachment site of .Speed's Test is used to test for superior labral tears or bicipital tendonitis. Technique [edit | edit source] To perform the Speed's Test, the examiner places the patient's arm in shoulder flexion, external rotation, full elbow extension, and forearm supination; manual resistance is then applied by the examiner in a downward direction.
Physical examination included the apprehension, relocation, load and shift, inferior sulcus sign, and crank tests. Shoulder arthroscopy confirmed labral tears in 41 patients (76%). Magnetic resonance imaging produced a sensitivity of 59% and a specificity of 85%. Physical examination yielded a sensitivity of 90% and a specificity of 85%. A Bankart lesion or glenoid labrum tear happens when your shoulder bone dislocates and tears the supportive tissues around it. A dislocated shoulder is a traumatic injury caused by significant force. . They’ll follow up with imaging tests to see the injury. Tests usually include X-rays and an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). They’ll want .Surgery for a shoulder labral tear usually takes an hour and is an outpatient procedure. Our fellowship-trained, internationally known orthopedic surgeons typically use arthroscopic surgery, also called arthroscopy, which is performed through three or four small incisions, rather than one large open incision. .The two most common physical examination tests to identify shoulder labrum injury are the O’Brien Test and Speed’s Test: O’Brien Test (Active Compression Test): Procedure: The patient stands with the shoulder flexed to 90 degrees and the elbow fully extended. The arm is then adducted 10-15 degrees across the body, and the thumb is pointed .
Superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tears are a subset of labral pathology in acute and chronic/degenerative settings. First described in the 1980s, extensive study has followed to elucidate appropriate evaluation and management.[1] Patient-specific considerations and appropriate utilization of both non-surgical and surgical interventions are of the utmost .
Portable Digital Chemical Moisture Meter suppliers
WEBDomingo, 07/04. Campeonato Norueguês: jogos ao vivo, placar ao vivo da rodada, jogos de hoje, jogos de ontem e resultados online. Classificação atualizada e tabela completa .
shoulder tests labral tears|positive shoulder labral tear test